What Do Auditor Do?
Job Description: Examine and analyze accounting records to determine financial status of establishment and prepare financial reports concerning operating procedures.
Daily Life Of an Auditor
- Examine records and interview workers to ensure recording of transactions and compliance with laws and regulations.
- Inspect cash on hand, notes receivable and payable, negotiable securities, and canceled checks to confirm records are accurate.
- Examine inventory to verify journal and ledger entries.
- Examine whether the organization’s objectives are reflected in its management activities, and whether employees understand the objectives.
- Direct activities of personnel engaged in filing, recording, compiling, and transmitting financial records.
- Examine records, tax returns, and related documents pertaining to settlement of decedent’s estate.
Featured schools near , edit
What Skills Do You Need to Work as an Auditor?
Auditors state the following job skills are important in their day-to-day work.
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Writing: Communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs of the audience.
Speaking: Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Complex Problem Solving: Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Other Auditor Job Titles
- Asset Analyst
- Insurance Auditor
- Assurance Manager
- Tax Specialist
- Staff Auditor
Job Demand for Auditors
There were about 1,397,700 jobs for Auditor in 2016 (in the United States). New jobs are being produced at a rate of 10% which is above the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 139,900 new jobs for Auditor by 2026. The BLS estimates 141,800 yearly job openings in this field.
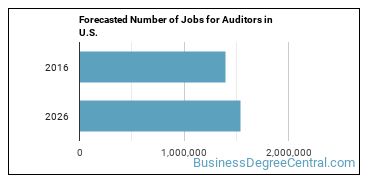
The states with the most job growth for Auditor are Utah, Colorado, and Tennessee. Watch out if you plan on working in Maine, Alaska, or Ohio. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
Auditor Salary
Auditors make between $43,650 and $122,840 a year.
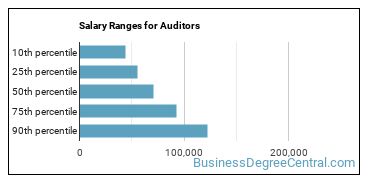
Auditors who work in District of Columbia, New York, or New Jersey, make the highest salaries.
How much do Auditors make in each U.S. state?
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $70,310 |
| Alaska | $82,920 |
| Arizona | $69,190 |
| Arkansas | $67,700 |
| California | $84,430 |
| Colorado | $82,320 |
| Connecticut | $84,890 |
| Delaware | $78,120 |
| District of Columbia | $98,130 |
| Florida | $71,790 |
| Georgia | $75,930 |
| Hawaii | $65,580 |
| Idaho | $66,110 |
| Illinois | $81,060 |
| Indiana | $70,780 |
| Iowa | $67,030 |
| Kansas | $66,530 |
| Kentucky | $67,080 |
| Louisiana | $66,860 |
| Maine | $70,810 |
| Maryland | $82,610 |
| Massachusetts | $81,460 |
| Michigan | $74,370 |
| Minnesota | $72,480 |
| Mississippi | $62,850 |
| Missouri | $70,240 |
| Montana | $66,410 |
| Nebraska | $67,920 |
| Nevada | $66,600 |
| New Hampshire | $72,690 |
| New Jersey | $90,400 |
| New Mexico | $66,370 |
| New York | $96,300 |
| North Carolina | $76,880 |
| North Dakota | $61,870 |
| Ohio | $72,370 |
| Oklahoma | $73,040 |
| Oregon | $71,450 |
| Pennsylvania | $75,250 |
| Rhode Island | $81,090 |
| South Carolina | $64,750 |
| South Dakota | $65,800 |
| Tennessee | $69,690 |
| Texas | $80,200 |
| Utah | $70,980 |
| Vermont | $75,360 |
| Virginia | $85,640 |
| Washington | $78,970 |
| West Virginia | $68,160 |
| Wisconsin | $68,410 |
| Wyoming | $66,180 |
What Tools & Technology do Auditors Use?
Below is a list of the types of tools and technologies that Auditors may use on a daily basis:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Microsoft Access
- Data entry software
- SAP
- Microsoft Project
- Spreadsheet software
- Microsoft Visio
- Structured query language SQL
- Microsoft Dynamics
- SAS
- IBM Notes
- Microsoft Visual Basic
- Google Docs
- UNIX
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Intuit QuickBooks
- Oracle PeopleSoft
Becoming an Auditor
Education needed to be an Auditor:
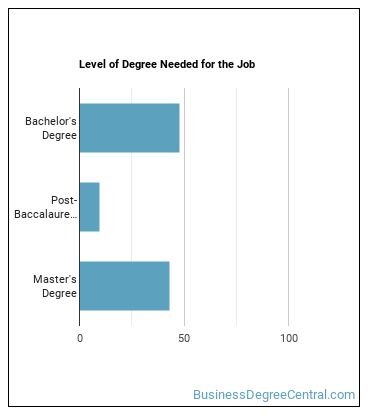
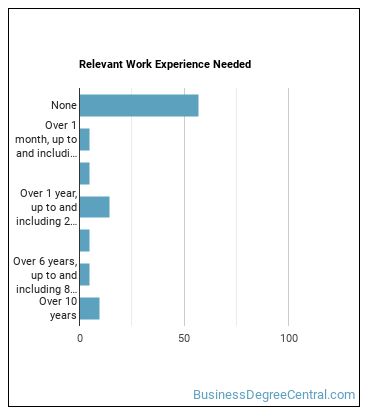
How many years of work experience do I need?
Auditors Sector
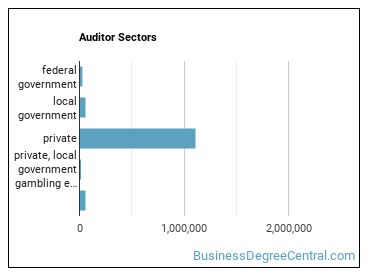
Auditors work in the following industries:
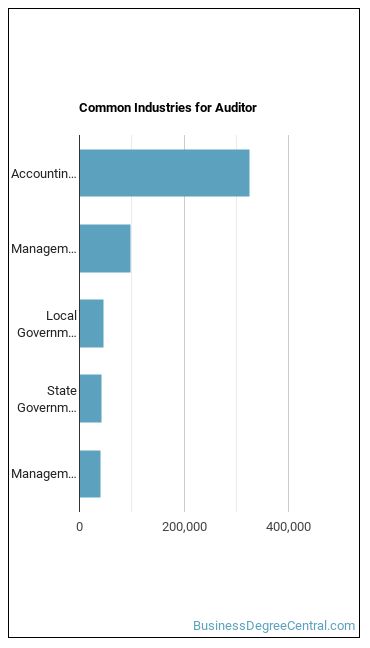
Other Jobs You May be Interested In
Those who work as an Auditor sometimes switch careers to one of these choices:
References:
Image Credit: Pixabay via CC0 License
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs.
Visit School
