What Do Energy Auditor Do?
Position Description Conduct energy audits of buildings, building systems, or process systems. May also conduct investment grade audits of buildings or systems.
What Do Energy Auditors Do On a Daily Basis?
- Analyze technical feasibility of energy-saving measures, using knowledge of engineering, energy production, energy use, construction, maintenance, system operation, or process systems.
- Collect and analyze field data related to energy usage.
- Examine commercial sites to determine the feasibility of installing equipment that allows building management systems to reduce electricity consumption during peak demand periods.
- Verify income eligibility of participants in publicly financed weatherization programs.
- Inspect or evaluate building envelopes, mechanical systems, electrical systems, or process systems to determine the energy consumption of each system.
- Perform tests such as blower-door tests to locate air leaks.
Featured schools near , edit
What Skills Do You Need to Work as an Energy Auditor?
These are the skills Energy Auditors say are the most useful in their careers:
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Writing: Communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs of the audience.
Speaking: Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Judgment and Decision Making: Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Related Job Titles
- Commercial Energy Rater
- Energy Manager
- Building Energy Consultant
- Resource Conservation Manager
- Energy Conservation Technician
Is There Going to be Demand for Energy Auditors?
In 2016, there was an estimated number of 1,023,900 jobs in the United States for Energy Auditor. New jobs are being produced at a rate of 8.8% which is above the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 90,400 new jobs for Energy Auditor by 2026. Due to new job openings and attrition, there will be an average of 104,200 job openings in this field each year.
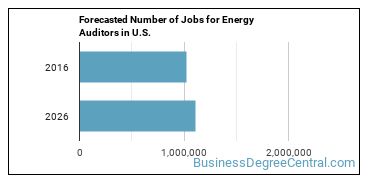
The states with the most job growth for Energy Auditor are Utah, Nevada, and Arkansas. Watch out if you plan on working in Alaska, Maine, or Oklahoma. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
What is the Average Salary of an Energy Auditor
The typical yearly salary for Energy Auditors is somewhere between $38,420 and $123,000.
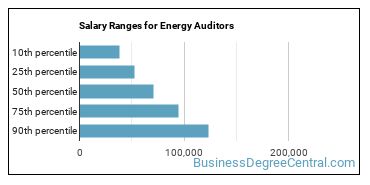
Energy Auditors who work in District of Columbia, Maryland, or Virginia, make the highest salaries.
How much do Energy Auditors make in different U.S. states?
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $85,140 |
| Alaska | $82,160 |
| Arizona | $67,670 |
| Arkansas | $59,530 |
| California | $83,470 |
| Colorado | $82,130 |
| Connecticut | $78,120 |
| Delaware | $81,880 |
| District of Columbia | $102,730 |
| Florida | $66,440 |
| Georgia | $75,070 |
| Hawaii | $73,310 |
| Idaho | $67,630 |
| Illinois | $71,780 |
| Indiana | $61,290 |
| Iowa | $65,020 |
| Kansas | $74,520 |
| Kentucky | $66,450 |
| Louisiana | $60,430 |
| Maine | $66,760 |
| Maryland | $91,400 |
| Massachusetts | $85,980 |
| Michigan | $70,410 |
| Minnesota | $71,220 |
| Mississippi | $65,650 |
| Missouri | $73,500 |
| Montana | $66,290 |
| Nebraska | $74,370 |
| Nevada | $71,580 |
| New Hampshire | $70,890 |
| New Jersey | $78,920 |
| New Mexico | $70,340 |
| New York | $83,330 |
| North Carolina | $74,040 |
| North Dakota | $73,010 |
| Ohio | $71,190 |
| Oklahoma | $72,940 |
| Oregon | $68,890 |
| Pennsylvania | $80,910 |
| Rhode Island | $80,380 |
| South Carolina | $69,340 |
| South Dakota | $70,830 |
| Tennessee | $62,330 |
| Texas | $80,140 |
| Utah | $72,100 |
| Vermont | $67,910 |
| Virginia | $88,180 |
| Washington | $77,850 |
| West Virginia | $70,180 |
| Wisconsin | $57,620 |
| Wyoming | $69,740 |
What Tools & Technology do Energy Auditors Use?
Although they’re not necessarily needed for all jobs, the following technologies are used by many Energy Auditors:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Microsoft Outlook
- Web browser software
- Python
- Microsoft Access
- SAP
- Autodesk AutoCAD
- Microsoft SharePoint
- Adobe Systems Adobe Photoshop
- Structured query language SQL
- The MathWorks MATLAB
- SAS
- Microsoft Dynamics
- Linux
- Microsoft Publisher
- Microsoft Visual Basic
- IBM SPSS Statistics
How do I Become an Energy Auditor?
Education needed to be an Energy Auditor:
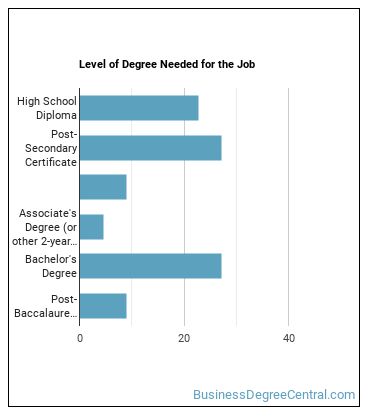
What work experience do I need to become an Energy Auditor?
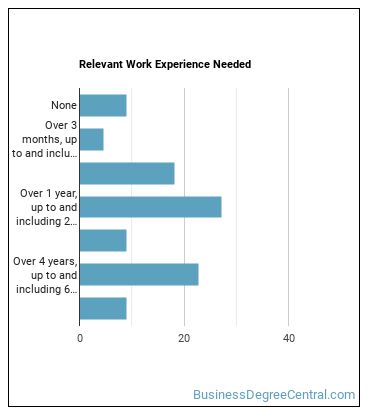
Where Energy Auditors Are Employed
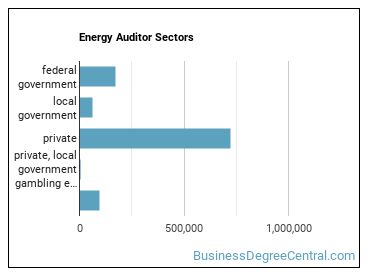
Below are examples of industries where Energy Auditors work:
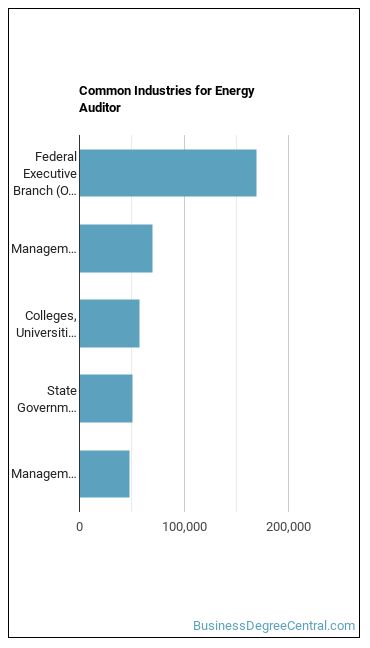
Other Jobs You May be Interested In
Those interested in being an Energy Auditor may also be interested in:
References:
More about our data sources and methodologies.
Featured Schools
You have goals. Southern New Hampshire University can help you get there. Whether you need a bachelor's degree to get into a career or want a master's degree to move up in your current career, SNHU has an online program for you. Find your degree from over 200 online programs.
Visit School
